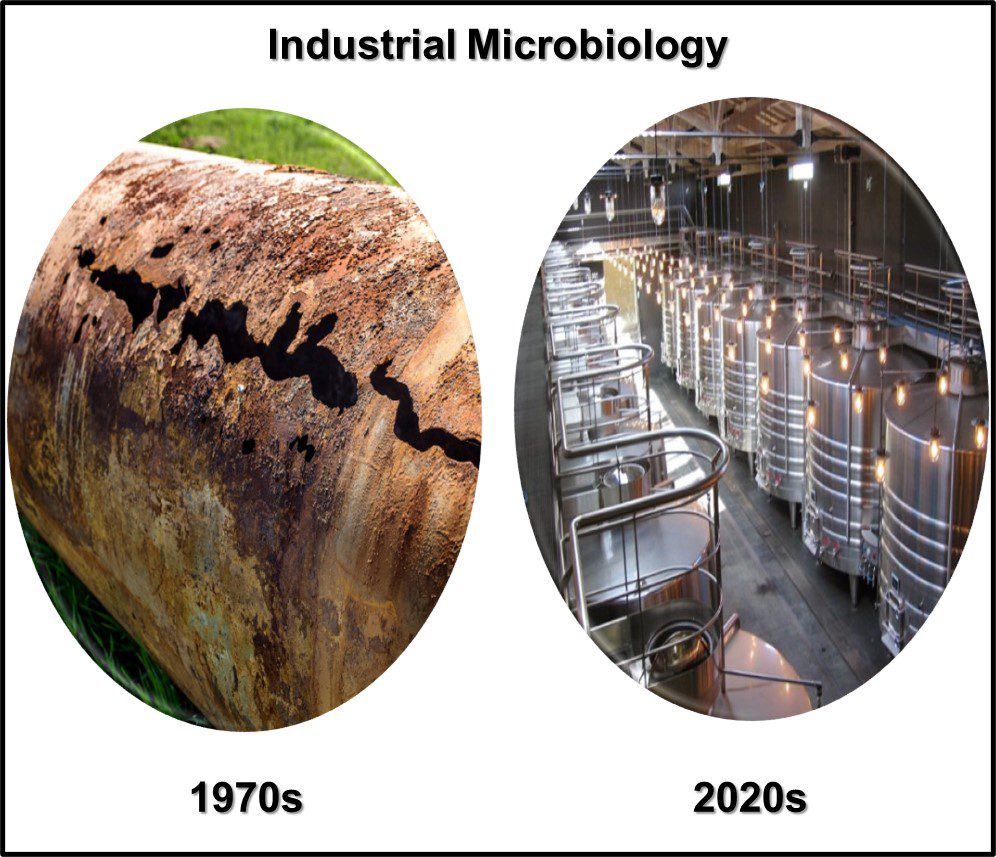
Left Image – microbiologically influenced corrosion of petroleum pipeline; Right Image – industrial scale fermentation.
Introduction
In a recent book chapter (Noha M. Sorour, et al. 2017. Chapter 3 – Microbial Biosynthesis of Health-Promoting Food Ingredients, In: Alexandru Mihai Grumezescu, Alina Maria Holban, Eds, In Handbook of Food Bioengineering, Food Biosynthesis, pp: 25-54, Academic Press, New York, ISBN 9780128113721,…